
Gluten may seem harmless, but for some people, it can silently wreak havoc on their health. Many individuals suffer from gluten intolerance or sensitivity without realizing it, as symptoms can be vague or mistaken for other health issues. Detecting gluten-related problems early can prevent long-term health complications and improve overall well-being.
If you experience unexplained symptoms, your body might be telling you that gluten is the culprit. Here are 12 signs that could indicate gluten sensitivity.
Video: Gluten Intolerance Symptoms (9 EARLY SIGNS You Are Gluten Intolerant!)
1. Hair Loss and Weak Hair Growth
Unexplained hair thinning or loss could be linked to gluten intolerance. The body requires essential nutrients like zinc, iron, and biotin for healthy hair growth. However, gluten-induced intestinal damage can cause malabsorption of these nutrients, leading to excessive shedding.
Many individuals with celiac disease or gluten sensitivity also experience alopecia areata, an autoimmune condition that results in patchy hair loss. A gluten-free diet has been shown to improve hair health in those affected.
2. Digestive Problems That Persist
One of the most common symptoms of gluten sensitivity is digestive distress, which can include bloating, nausea, diarrhea, constipation, and abdominal pain. These symptoms are often misdiagnosed as irritable bowel syndrome (IBS) or other gastrointestinal disorders.

If you frequently experience digestive discomfort after consuming foods containing gluten, your gut may be struggling to process it properly.
3. Unexplained Weight Fluctuations
Sudden weight loss or unexplained weight gain can be a sign of gluten intolerance. Gluten sensitivity triggers inflammation and disrupts metabolic function, leading to fluctuations in body weight.
In people with celiac disease, malabsorption can cause significant weight loss, while others with gluten sensitivity may gain weight due to inflammation-related bloating and fluid retention.
Video: 10 Surprising Signs You’re Actually Gluten Intolerant
4. Hormonal Imbalances and Irregular Cycles
Gluten intolerance has been linked to hormonal imbalances, especially in women. If you experience irregular menstrual cycles, severe PMS, or unexpected mood swings, gluten could be playing a role.
Hormonal fluctuations often worsen during puberty, pregnancy, and menopause, and gluten intolerance can make these changes even more challenging.
5. Brain Fog and Poor Concentration
Feeling mentally sluggish or struggling to focus? “Brain fog” is a common symptom of gluten sensitivity. Many people report difficulty concentrating, short-term memory problems, and mental fatigue after consuming gluten.
Gluten-related inflammation can also contribute to anxiety, depression, and insomnia, further impacting cognitive function.
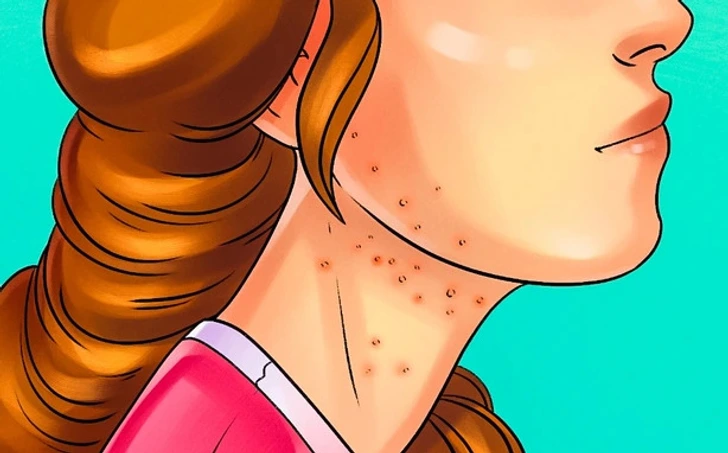
6. Skin Conditions Like Eczema and Rashes
If you struggle with itchy rashes, eczema, or psoriasis, gluten could be a hidden trigger. Some individuals with gluten sensitivity develop dermatitis herpetiformis, a painful, blistering rash associated with celiac disease.
A gluten-free diet has been shown to improve skin health, reducing inflammation and irritation.

7. ADHD-Like Symptoms
Studies suggest a link between gluten intolerance and attention deficit hyperactivity disorder (ADHD) symptoms, including difficulty concentrating, impulsivity, and hyperactivity.
Many individuals diagnosed with ADHD have found that eliminating gluten helps improve focus, reduce anxiety, and enhance overall mental clarity.

8. Weak Teeth and Frequent Cavities
Gluten intolerance can affect calcium absorption, leading to weakened tooth enamel, cavities, and gum disease. If you maintain good oral hygiene but still suffer from dental issues, gluten sensitivity might be a factor.
Dentists often see enamel erosion in patients with undiagnosed celiac disease. If you experience sensitive teeth or frequent mouth ulcers, it may be time to assess your diet.
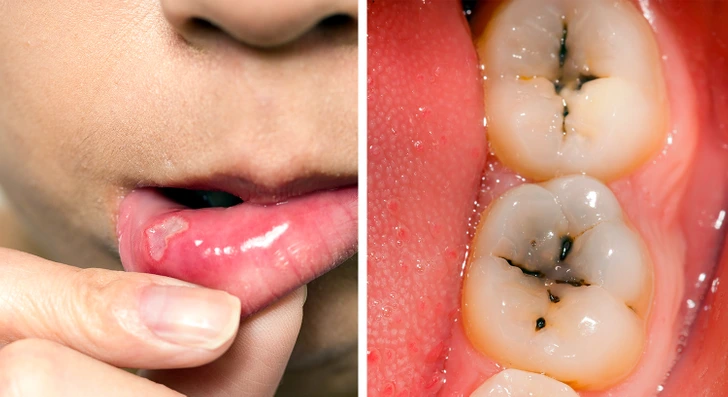
9. Chronic Iron Deficiency (Anemia)
Iron-deficiency anemia is common in people with gluten intolerance, especially those with celiac disease. Since gluten damages the small intestine, it reduces the body’s ability to absorb iron properly.
Video: Sykes-Picot: How and why Britain carved up the Arab world | Roy Casagranda | UNAPOLOGETIC
If you experience persistent fatigue, dizziness, or pale skin, an iron deficiency caused by gluten sensitivity may be to blame.

10. Autoimmune Diseases and Gluten Sensitivity
Many people with autoimmune diseases have a history of gluten intolerance, indicating a potential connection. Celiac disease itself is an autoimmune condition, but gluten sensitivity has also been linked to other autoimmune disorders, such as:
- Hashimoto’s thyroiditis (autoimmune thyroid disease)
- Lupus
- Rheumatoid arthritis
- Multiple sclerosis (MS)
Avoiding gluten can sometimes help reduce inflammation and improve symptoms in those with autoimmune disorders.
11. Tonsil Stones and Chronic Throat Issues
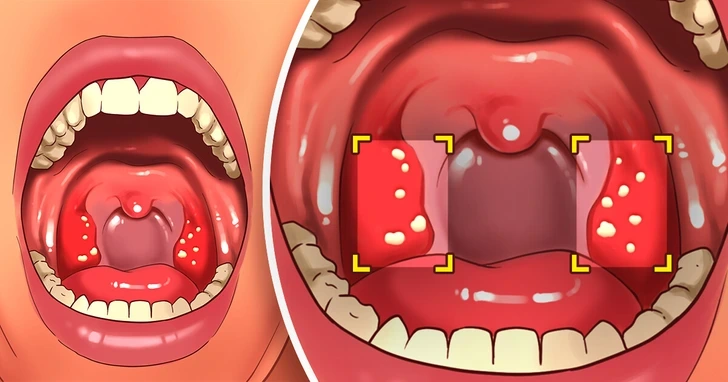
While not widely researched, some people with gluten sensitivity report frequent tonsil stones. Tonsil stones form when food particles and bacteria accumulate in the tonsils, leading to bad breath and discomfort.
Interestingly, individuals who eliminate gluten from their diet often notice a significant reduction in tonsil stones, suggesting a possible link between gluten and throat health.
12. Joint and Muscle Pain Without a Clear Cause
Experiencing chronic pain, stiffness, or muscle aches despite no obvious injury? Gluten-related inflammation may be affecting your joints and muscles.
Gluten has been linked to fibromyalgia-like symptoms, including body pain, fatigue, and muscle weakness. Many people with undiagnosed gluten sensitivity find significant relief from joint pain after removing gluten from their diet.
If you suspect gluten is causing your symptoms, here’s what you can do:
- Get Tested: Consult a doctor for a celiac disease test or a gluten sensitivity assessment. Keep in mind that standard tests may not always detect non-celiac gluten sensitivity.
- Eliminate Gluten from Your Diet: Remove foods containing wheat, barley, and rye. This includes bread, pasta, baked goods, and many processed foods.
- Look for Hidden Sources of Gluten: Gluten is often found in sauces, dressings, and processed snacks, so always read ingredient labels carefully.
- Monitor Your Symptoms: Keep a journal to track how your body responds after removing gluten. Many people notice improvements within a few weeks.
Gluten intolerance manifests in various ways, from digestive problems to neurological symptoms and autoimmune reactions. While some individuals experience obvious signs, others may suffer from silent symptoms that gradually worsen over time.
If you suspect gluten is impacting your health, listen to your body and consider making dietary changes. By identifying and eliminating problem foods, you can improve your energy levels, mental clarity, and overall well-being.


